Wan-Yu Tsai
Research Focuses
Electro-chemo-mechanical coupling behaviors of energy storage materials
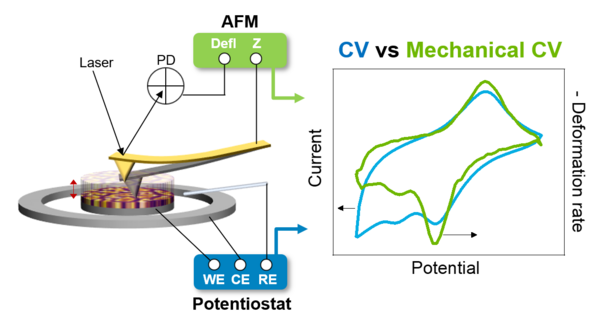
Both batteries and supercapacitors involve electrolytic ion insertion (or intercalation) into the electrodes, which often induces volume change. There is a strong correlation between the amount of electrode volume change induced by the ion insertion and its electrochemical performance (energy density; power density and cycle life). However, this mechano-electrochemical relationship is complex and intertwined. Our group monitors the current-strain correlation via operando AFM at the local level (nanometer scale) to investigate electro-chemo-mechanical coupling behaviors of the insertion-type electrodes.
Selected ref: Wan-Yu Tsai, Ruocun Wang, Shelby Boyd, Veronica Augustyn and Nina Balke, "Probing local electrochemistry via mechanical cyclic voltammetry curves" Nano Energy, 81, 105592 (2021)
Understanding and controlling the interfaces in solid-state batteries
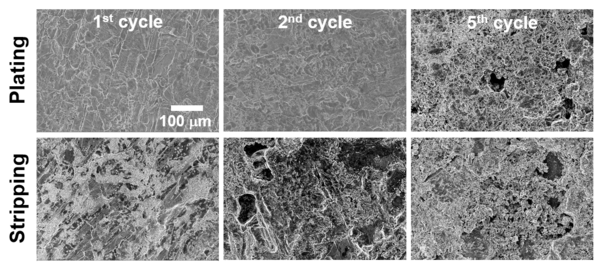
To enable the high energy alkali metal solid-state batteries, different classes of solid electrolytes were developed to create a physical barrier and prevent thermal runaway caused by alkali metal dendrite growing and shorting the cell. However, both anode and cathode undergo different degree of volume changes during cycling. Maintaining the solid-solid contact at various interfaces and achieving uniform alkali metal plating and stripping are the major challenges to enable alkali metal solid-state batteries. Our group focuses on monitoring the Li morphological change at different states of charge, understanding which properties controls the morphology, and how it affects the electrochemical performance.
Selected ref: Wan-Yu Tsai, Xi Chelsea Chen, Sergiy Kalnaus, Ritu Sahore, Zhijia Du, Andrew S. Westover, "Li morphology evolution during initial cycles in a gel composite polymer electrolyte" ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 5, 9, 11362–11369 (2022)