
Mohamed Elati
Axes de recherche
Research interests
Mohamed Elati is currently Professor of computer science at the Faculty of Pharmacy of Lille and the head of DISCO team "Digital systems and computational cancer" at Canther laboratory (UMR9020 CNRS - U1277 Inserm). He has worked for 20 years at the boundary of two disciplines: machine learning and systems biology. He has developed and will use various approaches to foster creative relationships between researchers originating from various disciplines, through both research and teaching sessions. M. Elati is the coordinator of the INSERM-ITMO LIONs project (2015-2019) providing an appropriate background for cancer systems biology; the ANR coordinator of the EU Chist-ERA AdaLab project (2014-2018) initiating the closed-loop automation of yeast systems biology and co-PI of four INCA-PLBIO grants (Bladder: 2012-15; Glioblastoma: 2019-21; Lung cancer: 2021-25; and Pancreatic cancer: 2024-28).
Leveraging principles of systems biology and Artificial Intelligence techniques, our computational DISCO team (https://canther.fr/fr/equipe-systemes-digitaux-et-cancer-computationnel/) contribute to:
• Bridge the gap between high-throughput biological data production and analytical tools to enhance our understanding of the systemic principles of tumor biology.
• Investigate cell regulatory networks to unravel cancer tumorigenesis, cellular heterogeneity, and therapy resistance.
• Develop and disseminate AI-powered Bio-IT tools that scientists can readily understand, trust, and effectively utilise for biological investigations.
Towards these goals, we design and develop new algorithms and software for building and analyzing regulatory networks from ‘omics’ data, network-based interpretation and integration of biological systems, network causality, and network-based hypothesis generation. Our approaches range from machine learning, evolutionary computation, and knowledge representation to closed-loop bioscience automation. We collaborate closely with experimental groups and share our tools as free, open-source packages and web applications. e.g., network inference/reconstruction: LICORN/CoRegNet, PreCisIon; network analysis/interrogation: PEPPER, skyclust, LatNET, cRegMap; network intervention/revision: Adalab, CoRegFlux, GREAT.
Funded Projects
Europe :
- 2021-2024 : GREENER: Gene and Regulatory Elements Networks Involved in Rice Root Tissue Differentiation. - PRCI ANR/FNR - Coordinators Dr. Christophe Perin (CIRAD, Montpellier), Role : PI Univ. Lille-CANTHER (own funding 195K€).
- 2015-18: Adaptive « Automated Scientific Laboratory - AdaLab » - CHIST-ERA - Coordinators Prof. Larisa Soldatova (Brunel University), Prof. Ross King (Univ. of Manchester) – 1300 K€. Role : ANR coordinateur, PI UEVE-iSSB (198K€).
- 2012-15: “A system biology approach to dissect cilia function and its disruption in human genetic disease” - SYSCILIA (EC FP7 - Health Cooperation programme). Coordinator Dr. Ronald Roepman (Univ of Nigmegen) – €1200K. Role: PI UEVE-iSSB (200K€)
National :
- 2022-24: NETMET: Regulation network of the oncogene addiction triggers by MET receptor in lung cancer, INCa PLBIO. Role PI Univ. Lille-CANTHER (own funding: 58 K€)
- 2018-22: INTEGRIN: Systems biology of integrin inhibition-induced apoptosis for novel glioblastoma treatment, INCa PLBIO, Grant N2017-145. Role PI Univ. Lille-CANTHER (own funding: 115 K€)
- 2015-19: LIONs: Large-scale Integrative approach to unravel the relationships between differentiatiON and tumorigenesiS. ITMO cancer/INSERM 2015 - coordinator: Mohamed Elati 750 K€. Role: coordinator PI Univ Lille-CANTHER (220K€)
- 2016-19: CHASSY: From multi-scale modeling of biological network to engineering metabolic circuits in a biotechnology chassis, Paris-Saclay IDEX, Grant Programme Interdisciplinaire IDI (co-PI), Horizon 2020 No 720824
- 2014-16: « Ingénierie robuste et évolution dirigée de voies métaboliques synthétiques par intégration des approches génomique » coordinator. Dr. François Jean-Marie (INSA Toulouse) – 500€K Rôle: co- PI François Képès (170 K€).
- 2013-14: “Comparaison de Réseaux de régulation par Enumération de PErturbations - CREPE (PEPS CNRS). Coordinator Pr. Etienne Birmelé (Univ. Paris 5) - 20 K€. Rôle: PI UEVE-iSSB (8K€)
- 2011-13: “Search for new therapeutic targets through the Identification of Networks Specifically altered during tumorIGenesis” - INSIGht (INCa). Coordinator Dr. François Radvanyi (Institut Curie) – €464K. Rôle: PI UEVE-iSSB (115 K€)
CANTHER-XAI platform and software packages
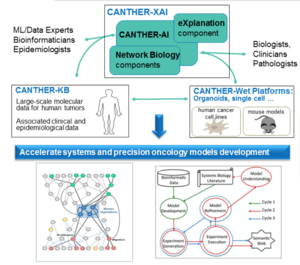
- CoRegFlux: R Bioconductor package (Trejo el al., BMC Systems Biology2017, Coutant et al., PNAS 2019). Integrating transcriptional activity in genome-scale models of metabolism.
- LatNet : R package (Dhifli el al., BMC Bioinformatics 2018). Latent
- network-based representations for large-scale gene expression data analysis.
- CoRegNet: is an R bioconductor package, which enables learning of gene regulatory networks from transcriptome data and infers master regulators controlling the transition between phenotypes. (Download stats: https://bioconductor.org/packages/stats/bioc/CoRegNet/).
- PEPPER: is a plugin cytoscape, which enables finding pathways connecting a protein set within a PPI-network using multi-objective optimization. Published in 2014 (Download stats: apps.cytoscape.org/download/stats/pepper/)
- GREAT : The Genome REgulatory and Architecture Tools (GREAT). GREAT is a software suite of related and interconnected tools, currently able to perform systematic analyses of genome regularities (GREAT-Scan-Pattern) as well as improve TFBS prediction based on gene position information (GREATScan- PreCisIon).
Collaborators
Postdocs
- Constantinos Yeles, ANR GREENER
- Maria Kondratova, INCa PLBIO
Current PhD Students
- Geoffrey Palwak (with David Tulasne, ANR AI_PhD@Lille)
- Liangwei YIN (with Christophe Battail, EU Caty)
Former collaborators
Former Postdoc
- Wajdi Dhifli (assistant professor, Lille)
- Daniel Trejo Banos (Researcher, Swiss data science center)
- Konstantinos Koutroumpas (Patent examiner, EU Patent Office)
- Cuong TO (assistant professor, Vietnam)
Former PhD students
- Pauline Trebulle (Post-doc, Crick Institute, London)
- Rémy Nicolle (Team leader INSERM)



